You know that feeling when you’re staring at a set of electrical plans and everything kind of blurs together? Lines, symbols, notes in tiny text. Someone says, “It’s all standard,” and you nod, but inside, you’re not totally sure what you’re looking at. Yeah. That moment.
Residential electrical plans sound technical, intimidating, and boring at first glance. But these plans are where comfort, safety, and sanity start. They decide whether your lights make sense, your outlets are where you actually need them, and whether you’re stripping into drywall 6 months later, thinking, Who planned this?
Whether you’re a homeowner planning a build, a contractor with subcontractors, or a designer trying to avoid coordination issues, electrical plans matter more than you think.
So let’s slow it down. Through away the confusion and talk about residential electrical plans in detail!
If you want to learn how spaces are categorized in residential design, this guide on types of rooms in a house explains it well.
What Is an Electrical Blueprint?
Think of an electrical blueprint as the nervous system of a house. Walls and framing are the bones, plumbing is the veins. And electrical? That’s what makes the place feel alive. Lights turn on, devices charge, and appliances work without tripping breakers every five minutes.
An electrical blueprint, also called an electrical drawing plan, is a detailed map showing:
- Where power comes into the house
- How it’s distributed
- Where fixtures, switches, and outlets live
- How everything connects back to the panel
It’s not just about putting in an outlet, but also involves:
- Why does it go there?
- What circuits is it on?
- And how it stays safe under load.
Simply put, you can’t take it as an option if you want inspections to pass, if you want electricians to stay on schedule, and if you want to avoid expensive rework. Also, don’t ensure that they look pretty, but focus on their precision. Once you learn how to read them, they stop feeling mysterious.
If you’re new to technical drawings, this article explains what architectural drafting is and how plans are developed.
Components of Residential Electrical Plans
Every solid set of residential electrical plans includes a few core elements. If you miss one, the things start to shake.
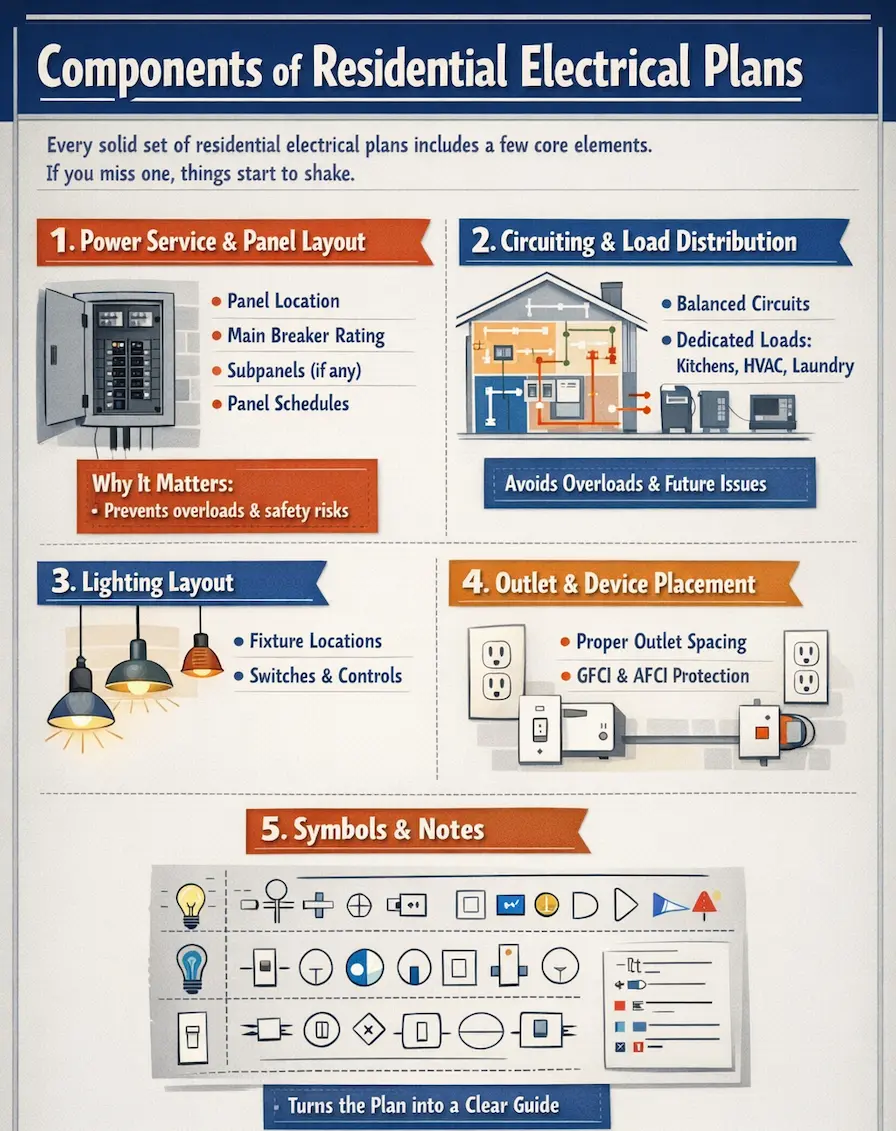
1. Power Service and Panel Layout
This is ground zero. The plan shows where power enters the home and how it feeds into the main service panel. You’ll see:
- Panel location
- Main breaker rating
- Subpanels (if any)
- Panel schedules listing each circuit
Why does this matter?
Because everything else depends on it, including overloaded panels, leads to nuisance tripping, heat buildup, and safety risks.
2. Circuiting and Load Distribution
This is where planning saves you real money. A proper electrical diagram shows how loads are balanced across circuits. Kitchens, bathrooms, HVAC, laundry, these areas draw serious power and often need dedicated circuits.
Good plans help you avoid:
- Overloaded breakers
- Future capacity issues
- Inspector red flags
And, if your plans are bad, you will push problems downstream.
3. Lighting Layout
Lighting plans show fixture types, switching locations, and control methods. That includes:
- Recessed lights
- Pendants
- Ceiling fans
- Dimmers and smart controls
4. Outlet and Device Placement
Outlets aren’t random; they must be planned before installation. Well, electrical plans account for:
- Code-required spacing
- Furniture layouts
- Appliance locations
- GFCI and AFCI protection
Inspectors and you don’t want extension cords everywhere, and it is where right outlet and device placement play the game.
5. Symbols and Notes
Electrical symbols look like a secret language until someone explains them. Circles, triangles, lines with slashes, they all mean something specific. You need to understand them, starting from scratch. Once you know the basics, the plan reads like a story instead of a puzzle.
To understand how electrical layouts fit within the full drawing set, read our guide to construction documents.
Common Electrical Symbols Explained
When people say electrical plans are confusing, they’re usually not talking about circuits; they’re talking about symbols. In other words, they’re talking about little circles, triangles, and lines with strange marks. It feels like someone forgot to include the decoder ring.
Reality is, electrical symbols aren’t complicated; they’re just unfamiliar.
An electrical symbol is a shortcut. Instead of writing duplex receptacle fifty times, the plan uses a symbol everyone in the trade recognizes instantly. That consistency is what keeps projects moving.
Some of the most common ones you’ll see:
| Symbols | Meanings |
| Outlet symbols | Usually circles or rectangles with small marks showing type: standard, GFCI, USB, or floor outlet. |
| Switch symbols | Marked with “S,” “3-way,” or “4-way” indicators |
| Light fixtures | Circles, crossed lines, or specialty icons for recessed, pendant, or surface lights |
| Panel symbols: | Typically, a labeled rectangle showing the service location |
| Home runs | Lines pointing back to the panel, showing where circuits originate |
Every professional electrical blueprint includes a symbol legend. That legend isn’t optional; it’s the key that turns confusion into clarity.
Pro Tip: Never assume symbols mean the same thing across every plan. Always check the legend. That’s how you avoid expensive misunderstandings.
How to Read the Symbol Key on Electrical Blueprints
Think of the symbol key like a map legend. Once you understand it, the entire drawing opens up. Start by scanning the legend before you look at anything else. This saves time every single time.
Here’s how professionals read it:
● Match Symbols Visually!
Don’t read descriptions yet. Just match the shapes you see on the plan to the shapes in the legend.
● Check Device Types and Ratings!
The legend often notes voltage, amperage, or protection requirements.
● Look for Variations!
A filled circle and an empty circle represent two different fixtures.
● Note Abbreviations!
“WP” for weatherproof. “GFI” for ground fault. Small letters, big consequences.
Once you get comfortable with this, an electrical drawing plan stops feeling like a puzzle. It starts reading like instructions, the main purpose of electrical drawings in any residential construction project.
Why You Need a Professional Electrical Drawing Plan
Professional electrical drawing plans aren’t about drawing; they’re about thinking ahead. A trained drafter or electrical designer:
- Understands code before it becomes a problem
- Knows where electricians lose time
- Anticipates inspection questions
- Designs for real-world use, and not theory
And when plans are done right, everyone downstream wins. Electricians install faster, inspectors approve smoother, and homeowners live more easily. If you are thinking about DIY, these plans often cost less upfront, but they many times cost more later.
To see how electrical work coordinates with mechanical and plumbing systems, learn what MEP means in construction.
NEC Compliance & Residential Electrical Plans
The National Electrical Code (NEC) isn’t a suggestion; however, it’s the baseline for safety in residential construction. Professional electrical blueprints are built around NEC compliance, including:
- Circuit protection rules
- Outlet spacing requirements
- Grounding and bonding standards
- GFCI and AFCI placement
Remember that the NEC changes. What passed ten years ago might not pass today. And when plans ignore current code, inspections are delay, projects are paused, and costs increase.
How to Schedule Panel & Map Circuit Breaker?
The panel schedule is the quiet workhorse of residential electrical plans. It doesn’t look exciting, but it’s doing a lot of heavy lifting. A panel schedule shows:
- Circuit numbers
- What each circuit feeds
- Breaker sizes
- Load types
This is how electricians know what goes where. It’s how inspectors verify compliance, and how future homeowners avoid guessing which breaker controls the garage freezer.
Good circuit mapping helps you avoid:
- Overloaded breakers
- Nuisance tripping
- Dangerous heat buildup
A professional electrical diagram ties every outlet, fixture, and appliance back to the panel logically. Kitchens, bathrooms, HVAC, and laundry loads are separated intentionally. When panel schedules are missing or sloppy, troubleshooting turns into trial and error.
The Difference Between Electrical Diagram & Wiring Diagram
People use these terms interchangeably. They’re not the same. An electrical diagram shows how a system functions conceptually; think of logic, flow, and relationships. On the other hand, a wiring diagram shows physical connections, including actual wires, paths, and terminations.
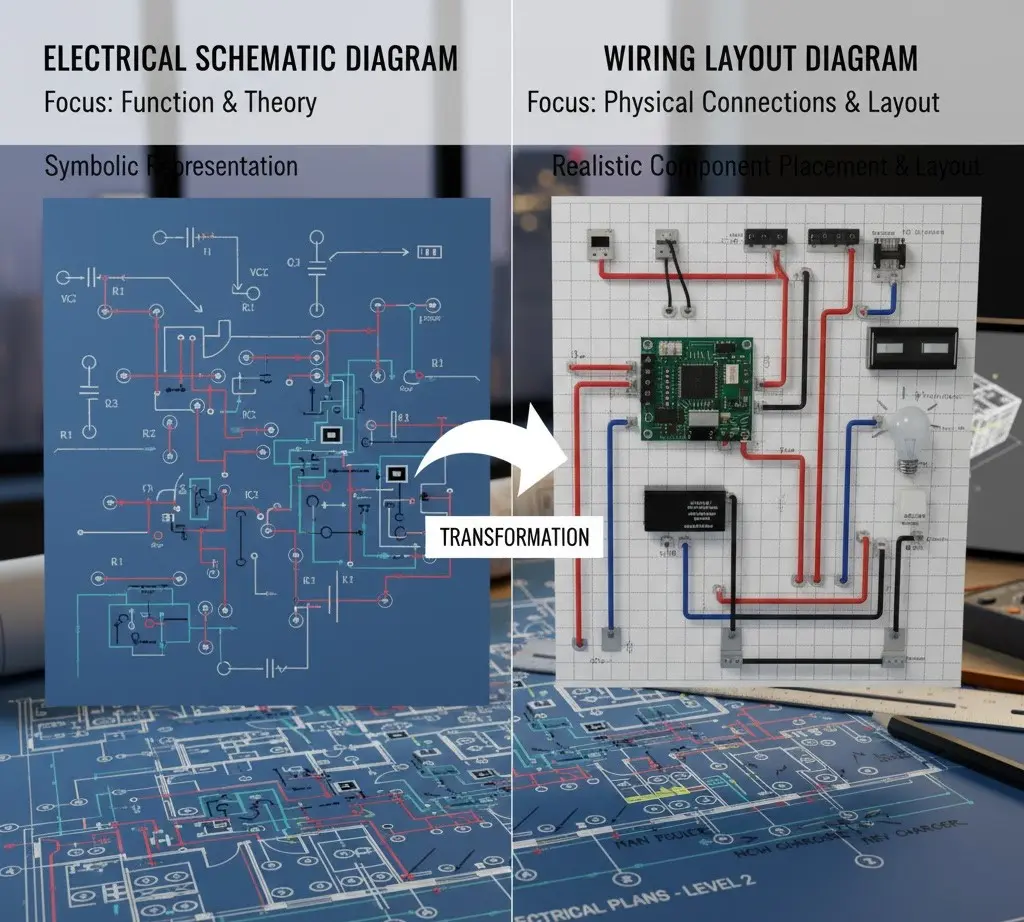
Here’s the simple way to remember it:
- Electrical diagram = how it works
- Wiring diagram = how it’s built
Residential electrical plans lean heavily on electrical diagrams, with wiring details referenced where needed. Both matter, and confusing them leads to mistakes.
How to Create a Residential Electrical Plan
Here’s how residential electrical plans are actually created.
- Start with the floor plan: Cover walls, doors, windows, and furniture layouts.
- Identify load-heavy areas: Cover kitchens, bathrooms, garages, and laundry rooms.
- Place lighting and controls: This is where usability matters. You’re planning how people move through the space.
- Add outlets and special devices: Code minimums first, and real-life convenience second. The best plans balance both.
- Assign circuits and panel connections: Everything gets tied back logically to the service panel.
- Apply NEC rules and local amendments: This is where experience shows. Codes aren’t just rules, but they’re taken as patterns.
All About Legends, Notes, and Annotations That Actually Help on Site
Plans fail when one assumes too much, and annotations are how you remove assumptions. Good electrical plans include notes that explain intent:
- Mounting heights
- Special installation conditions
- Coordination with HVAC or cabinetry
- Clarifications that prevent field guesses
This is especially important on residential projects where changes happen fast. A short note on paper can save hours on site. Above all, clear notes protect everyone, including designers, electricians, and homeowners; all benefit when intent is documented.
How CAD Drafters Can Help in Your Next Project
Professional CAD drafters translate ideas, codes, and requirements into precise, buildable documents. They live in the space between design intent and construction reality. When CAD drafters handle residential electrical plans, you get:
- Clear, standardized symbols
- Accurate scaling
- Coordination with architectural layouts
- Faster revisions when things change
More importantly, you get plans that electricians trust. This saves time and money.
Strategy Matters More Than Symbols
Anyone can learn symbols, but strategy making needs experience. Good electrical planning thinks about:
- How people actually live in the space
- How technology might evolve
- Where flexibility matters
- What future upgrades could require
That’s the difference between plans that just pass inspection and plans that still need amendments to meet current local building codes.
Room-by-Room Electrical Planning
Not every room behaves the same electrically. Here’s what good planning looks like, room by room.
| Room Type | Specifications |
| Kitchen |
|
| Bedroom |
|
| Bathroom |
|
| Living Area |
|
| Garage |
|
Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Some mistakes show up again and again in residential projects:
- Too few outlets
- Poor switch placement
- No allowance for future loads
- Incomplete panel schedules
- Ignoring furniture layouts
To fix them, thoughtful planning early is required, before walls go up and wires get pulled.
How to Read Electrical Plans Before Construction Starts
Before construction begins, plans deserve a slow read. Here’s how to review them without being an expert:
- Walk room by room on paper
- Imagine turning lights on and off
- Ask where you’d charge a phone
- Look for missing outlets
- Check panel locations
This is your last easy chance to make changes. Once wires are pulled, every correction costs more.
Real World Residential Electrical Plan Example
Imagine a simple three-bedroom home. The panel sits near the garage. Kitchen circuits are separated. Bedrooms share lighting circuits but not outlets. Bathrooms have dedicated receptacle circuits. Exterior outlets are weather-protected and clearly labeled.
Nothing fancy and nothing overdesigned. But everything makes sense, which is the goal of a good electrical blueprint.
The Real Cost of Cutting Corners
Revisions after construction start cost more. Every missing outlet becomes drywall repair; every misrouted circuit becomes labor hours; and every failed inspection becomes schedule issues. A solid electrical drawing plan is insurance, which pays off when things don’t go wrong.
How to Ensure Future-Proofing of Your Home Electrical System
The smartest electrical plans include 5 steps ahead. Future-proofing includes:
- Spare panel capacity
- Conduit paths for upgrades
- EV charger allowances
- Low-voltage pathways
- Smart home integration readiness
You don’t need to install everything now. However, you just need to plan for it. That mindset saves thousands later.
Smart planning today means fewer rewires tomorrow. Get your home electrically ready for the future.
Conclusion
Residential electrical plans aren’t just technical documents; however, they’re decisions locked into walls. When they’re done right, you forget about them, but when they’re done wrong, you notice them every day.
If you’re planning a residential project and want electrical plans that are clear, compliant, and actually usable, work with professionals who understand both design and construction. CAD Drafters help turn electrical intent into plans builders trust and inspectors approve. If you’re ready to do it once and do it right, that’s the next move. Start your residential electrical planning with us now!
FAQs
How much does a residential electrical plan cost?
It depends on size, complexity, and level of detail. Small homes may cost a few hundred dollars. Larger or custom projects run higher. What matters more than price is accuracy, because fixing mistakes later costs far more.
Do I need electrical plans for renovations?
Often, yes, especially when adding circuits, upgrading panels, or altering layouts. Local permitting rules usually require updated electrical drawings.
Can electricians work without detailed plans?
They can, but it slows everything down. Clear plans reduce questions, change orders, and installation errors.
Are symbols the same across all electrical plans?
Most symbols follow industry standards, but legends matter. Always check the symbol key on each set of drawings.
When should electrical planning start?
Early. Ideally, alongside architectural design. Late-stage planning limits options and increases overall project cost.